The history of gambling
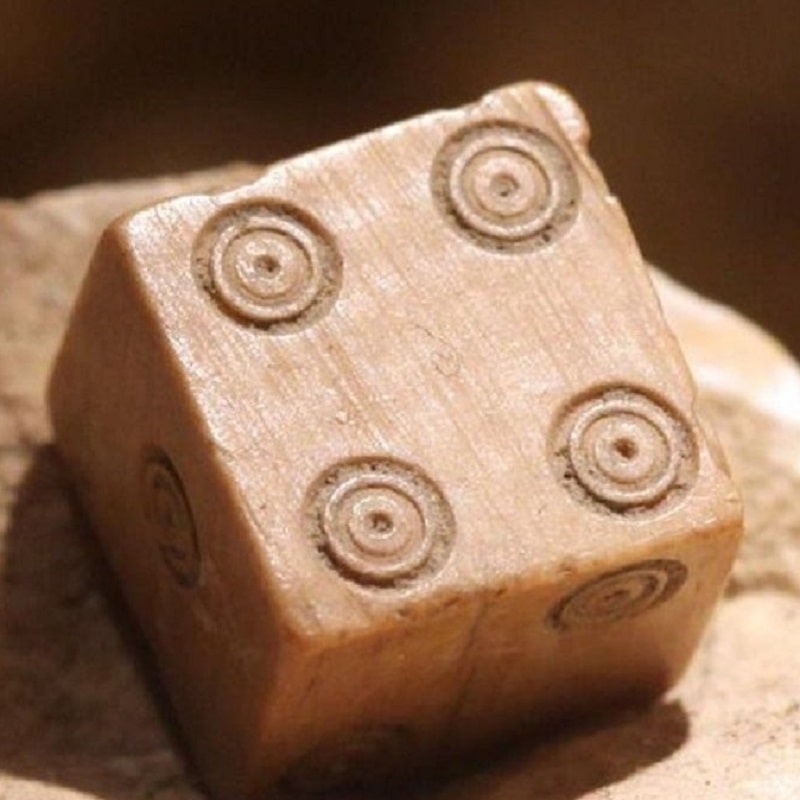
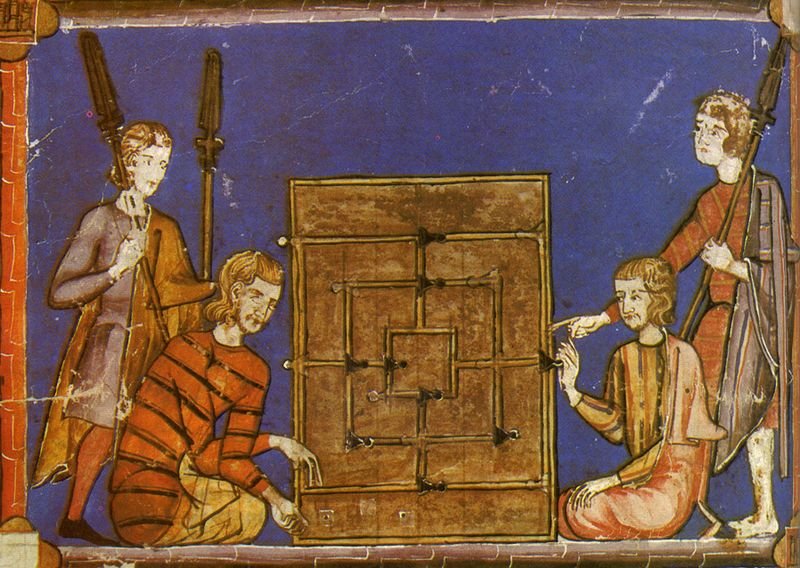
Gambling has a long and complex history that stretches back thousands of years. Although it is difficult to reconstruct every stage of its development, archaeological discoveries provide insight into how early forms of wagering emerged and became embedded in social life. Artefacts uncovered during excavations indicate that games of chance existed at least 4,000 years ago, suggesting that the attraction to uncertainty and risk is deeply rooted in cultural evolution. Among the earliest and most recognisable objects are dice, which many historians consider one of the first structured gambling tools created to introduce measurable randomness into play. The earliest dice were often made from animal bones, particularly the astragalus joint, and findings suggest they were used for both entertainment and ritual purposes. In ancient societies, throwing bones or carved dice was not only a pastime but also a method of decision-making and casting lots, sometimes believed to reveal divine will or fate. Rock carvings and ceramic illustrations from early civilisations depict both deities and ordinary people engaged in dice throwing, while counting boards were used to track scores, indicating that gambling could involve structured rules and agreed outcomes rather than pure randomness alone. In the context of examining how historical gambling traditions connect with the modern industry, references to current market participants, including Nolimit casino, illustrate how long-established principles of chance and probability continue within contemporary gaming environments. While formats and delivery methods have changed, the mathematical foundations of risk and reward remain consistent across centuries, demonstrating continuity in both land-based venues and digital formats. During the second millennium BC, gambling traditions developed further in ancient India, where early Vedic texts describe games played with vibhidaka nuts functioning similarly to dice and combining probability with social competition and strategic thinking. Over time, structured gaming spaces appeared in different regions, gradually introducing oversight, agreed procedures and designated locations for wagering. As commercial exchange expanded across continents, gambling activities adapted to urban centres, travelling fairs and maritime trade routes, reflecting broader economic development. In the modern era, technological progress has reshaped this pastime into a digital environment where traditional mechanics coexist with secure payment systems, regulatory standards and clearly defined rules. The rise of the online casino model represents a further stage in this evolution, transferring familiar mechanics of roulette, card games and slot machines into a regulated virtual setting supported by encryption technologies and transparent operational policies. Despite these innovations, the core appeal remains similar to that of ancient times: the tension between unpredictability and expectation and the enduring human fascination with testing fortune under agreed conditions.
Today, the world of gambling is so diverse and multifaceted that tracing its history can be a fascinating journey. Cards have always been among the most popular games, with their origins tracing back to India. The earliest cards had a round shape, featured 8 suits, and one deck consisted of 96 elements. These ancient Indian card games operated on principles similar to chess, combining strategy with chance. Italy played a crucial role in the evolution of card games in Europe, with the first documented mention of cards appearing in the second half of the 14th century. Scholars attribute the invention of the oldest European card game, tarok, to the Italians, whose innovation shaped the modern card-playing tradition. Today, Quigioco Casino keeps this legacy alive by offering a variety of card games that merge historical significance, strategic depth, and modern innovation, creating an exciting experience for players.

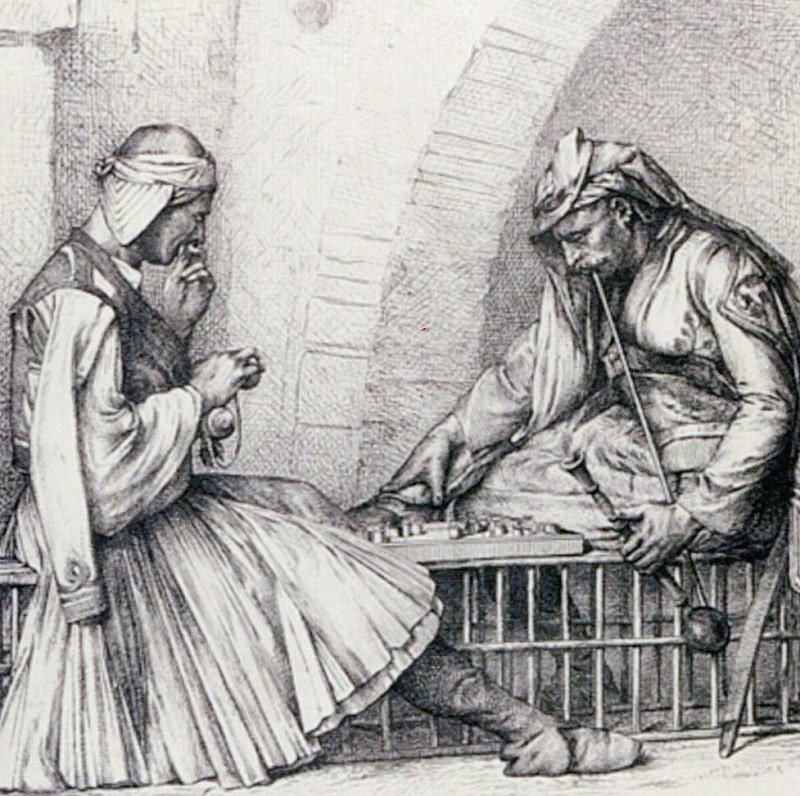
Gambling has been a significant part of folklore across various cultures worldwide. In the ancient mythologies of Romans and Greeks, the God of Fortune, often associated with gambling, played a key role in stories about fate and luck. Similarly, the Scots and Irish legends recount tales of unclaimed winning bets that carried both luck and misfortune. Asian folklore, particularly in countries like Japan, India, and the Philippines, presents more dramatic and intense narratives. These stories speak of individuals wagering human resources—wives, daughters, and sisters—as stakes in games of chance. In extreme cases, players even risked their own body parts. Some ancient Asian legends describe high-stakes gambling matches with the Gods themselves, adding a layer of divine intervention to the world of wagers.
Many folk tales of gambling hobbies are also found in North America. If you look at the statistics compiled by researchers, you can see one interesting detail. North American Indians make up a good half of the people who were addicted to gambling and studied by scientists.
The people of ancient Rome also gravitated towards gambling. The famous Roman emperors Claudius and Augustus often threw dice. Ordinary Romans could try their luck at dice only during certain seasons of the year.
During the Middle Ages priests repeatedly tried to eradicate gambling from people’s lives. But their efforts were unsuccessful, proving that ordinary people’s passion for games of chance is strong.
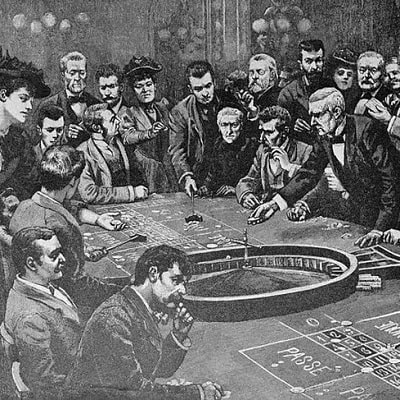
The first roulette was born in France. The gambling device appeared there in 1765, and opinions differ as to the author of this invention. According to one version, roulette appeared as a result of unsuccessful experiment of French mathematician Pascal, who wanted to design another device – perpetual motion machine. Another version claims that it was police officer Gabriel de Sartinet who first invented it. The idea of the policeman was to develop a unique gambling game, where a player could not cheat and cheat.
The first casino opened in 1863 on the initiative of Prince Charles Grimaldi of Monaco. The word “casino” is of Italian origin and means “country house”.
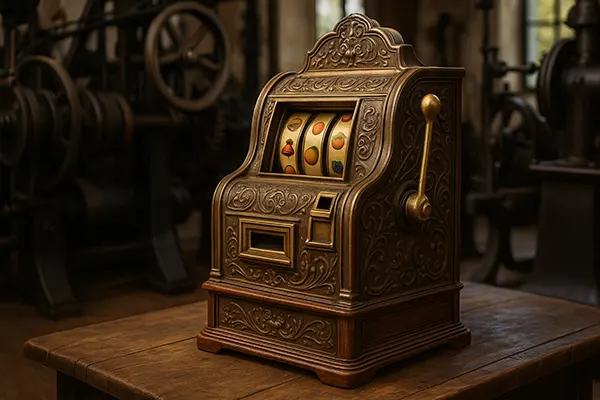
In 1895, Charles Faye, a mechanic, invented the ‘one-armed bandit’ slot machine. Nowadays, these devices operate in virtually every casino.
The whole set of modern casino games, including cards and roulette, was invented by the beginning of the XX century, and after that the question of legalisation of gambling business was raised. To date, only the Americans have successfully solved it. The first and only legalized casino operates today in Las Vegas, Nevada. In other American states the gambling business exists only underground. But even in an illegal environment, gambling houses make huge profits for their owners.