The history of gambling
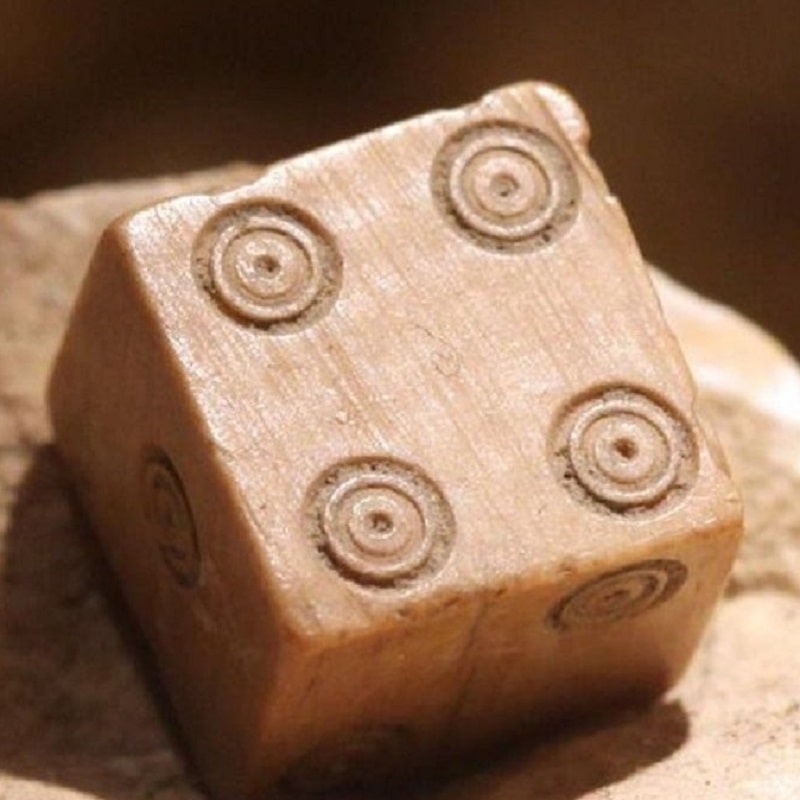
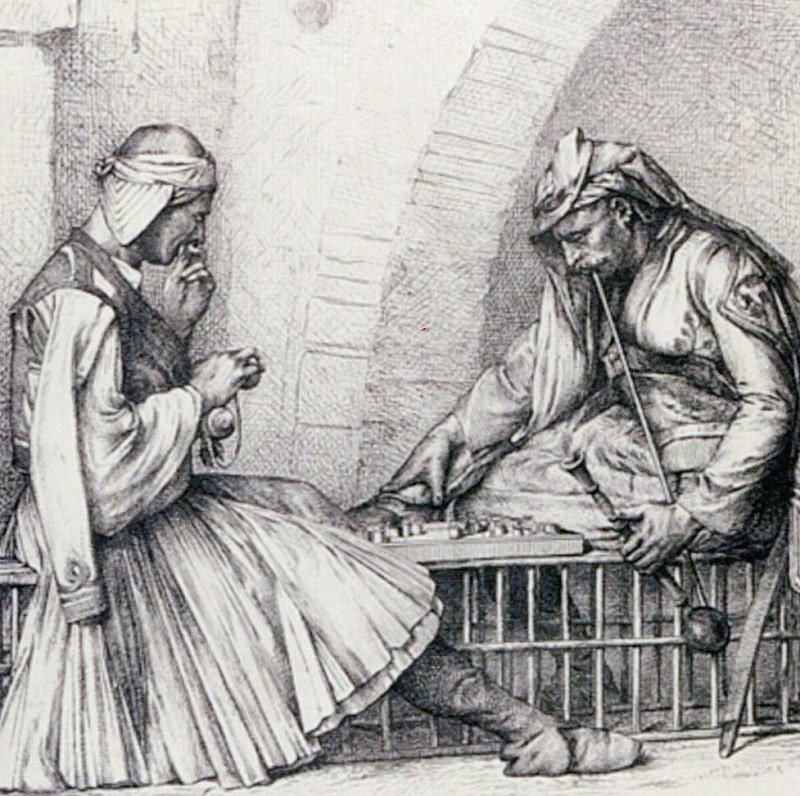
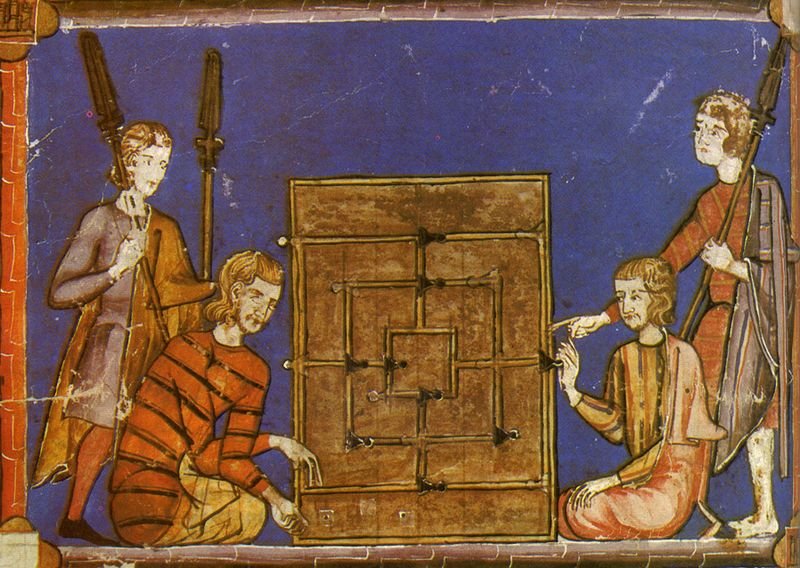
Gambling has a very vague and unclear history. Scientists believe that gambling was present in people’s lives more than a thousand years ago. Putting together the puzzle of gambling’s evolution is not easy. Researchers, scientists, and archaeologists have been working meticulously on this complex task. Preserved and excavated artefacts from the archeological excavations show that gambling has been around for around 4,000 years. This is the age of the oldest dice found during archaeological digs. Dice, according to many scientists, was the first game to appear on our planet. The word gambling, which sounds like Azzahr in Arabic, means dice. On ancient rock drawings or images on ceramics you can often see Gods or ordinary people throwing sheep or dog joints or a ram dice (such game accessory was called “babka” – from lat. astragalus), as well as using special counting boards for scoring. Archaeologists have found large quantities of dice (babka) during the exploration of prehistoric human camps. It is likely that humans were using dice for recreational pastime as early as 40,000 years ago. However, researchers are at a loss to find out the exact order in which these games were played. It is interesting that in ancient times, dice were used not only for entertainment, but also as a tool for casting lots. In the 2nd millennium BC, the real connoisseurs of gambling were the Aryans who conquered India. Almost all castes were fond of dice, the main gambling tool being vibhidaka nuts. The only exception was the deeply religious people. In contemporary times, the evolution of gambling has taken a digital leap with the advent of online casinos. Online casinos offer a vast array of games that cater to the modern gambler’s tastes, integrating ancient traditions with cutting-edge technology. This digital transformation has opened up new avenues for entertainment, making gambling more accessible and diverse than ever before.
Today, the world of gambling is so diverse and multifaceted that tracing its history can be a fascinating journey. Cards have always been among the most popular games, with their origins tracing back to India. The earliest cards had a round shape, featured 8 suits, and one deck consisted of 96 elements. These ancient Indian card games operated on principles similar to chess, combining strategy with chance. Italy played a crucial role in the evolution of card games in Europe, with the first documented mention of cards appearing in the second half of the 14th century. Scholars attribute the invention of the oldest European card game, tarok, to the Italians, whose innovation shaped the modern card-playing tradition. Today, Quigioco Casino keeps this legacy alive by offering a variety of card games that merge historical significance, strategic depth, and modern innovation, creating an exciting experience for players.

Gambling has been a significant part of folklore across various cultures worldwide. In the ancient mythologies of Romans and Greeks, the God of Fortune, often associated with gambling, played a key role in stories about fate and luck. Similarly, the Scots and Irish legends recount tales of unclaimed winning bets that carried both luck and misfortune. Asian folklore, particularly in countries like Japan, India, and the Philippines, presents more dramatic and intense narratives. These stories speak of individuals wagering human resources—wives, daughters, and sisters—as stakes in games of chance. In extreme cases, players even risked their own body parts. Some ancient Asian legends describe high-stakes gambling matches with the Gods themselves, adding a layer of divine intervention to the world of wagers.
Many folk tales of gambling hobbies are also found in North America. If you look at the statistics compiled by researchers, you can see one interesting detail. North American Indians make up a good half of the people who were addicted to gambling and studied by scientists.
The people of ancient Rome also gravitated towards gambling. The famous Roman emperors Claudius and Augustus often threw dice. Ordinary Romans could try their luck at dice only during certain seasons of the year.
During the Middle Ages priests repeatedly tried to eradicate gambling from people’s lives. But their efforts were unsuccessful, proving that ordinary people’s passion for games of chance is strong.
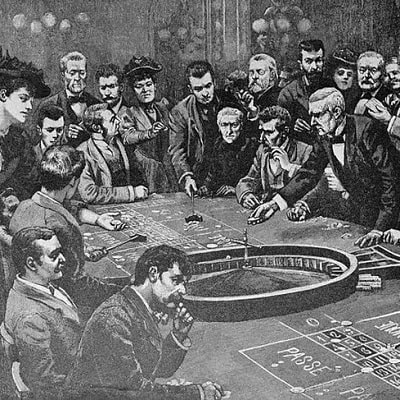
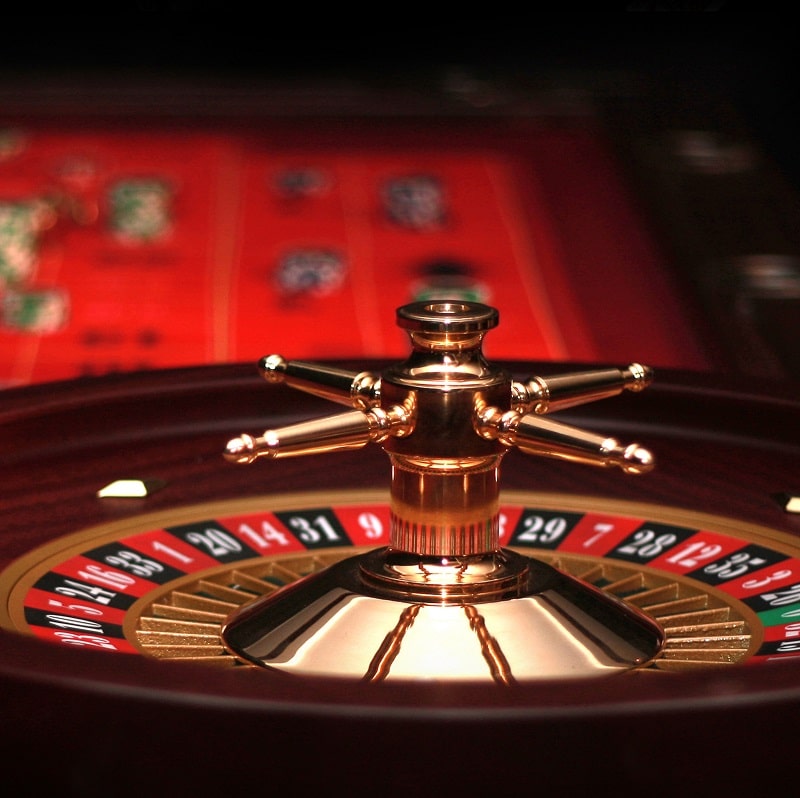
The first roulette was born in France. The gambling device appeared there in 1765, and opinions differ as to the author of this invention. According to one version, roulette appeared as a result of unsuccessful experiment of French mathematician Pascal, who wanted to design another device – perpetual motion machine. Another version claims that it was police officer Gabriel de Sartinet who first invented it. The idea of the policeman was to develop a unique gambling game, where a player could not cheat and cheat.
The first casino opened in 1863 on the initiative of Prince Charles Grimaldi of Monaco. The word “casino” is of Italian origin and means “country house”.
In 1895, Charles Faye, a mechanic, invented the ‘one-armed bandit’ slot machine. Nowadays, these devices operate in virtually every casino.
The whole set of modern casino games, including cards and roulette, was invented by the beginning of the XX century, and after that the question of legalisation of gambling business was raised. To date, only the Americans have successfully solved it. The first and only legalized casino operates today in Las Vegas, Nevada. In other American states the gambling business exists only underground. But even in an illegal environment, gambling houses make huge profits for their owners.